There are over 27 million cases of brain injuries around the world every year, which makes it the second most costly health condition.
Mortality rates for traumatic brain injury are 50%, with 67% of survivors being diagnosed with serious long-term disability.
Many brain injury patients develop a secondary brain injury which is often caused by brain hypoxia where brain cells die within minutes if deprived of sufficient oxygen.
When brain hypoxia is detected early, treatment to maintain adequate brain oxygen levels and prevent secondary brain injury are straight forward and effective; improving mortality and reducing long-term disability.
To date, brain hypoxia has been monitored through either invasive surgical procedures, or unreliable cerebral monitors.
This has limited the access to reliable information available to clinicians, placed increased strain on intensive care resources, impacted diagnosis accuracy, and extended patient stays.
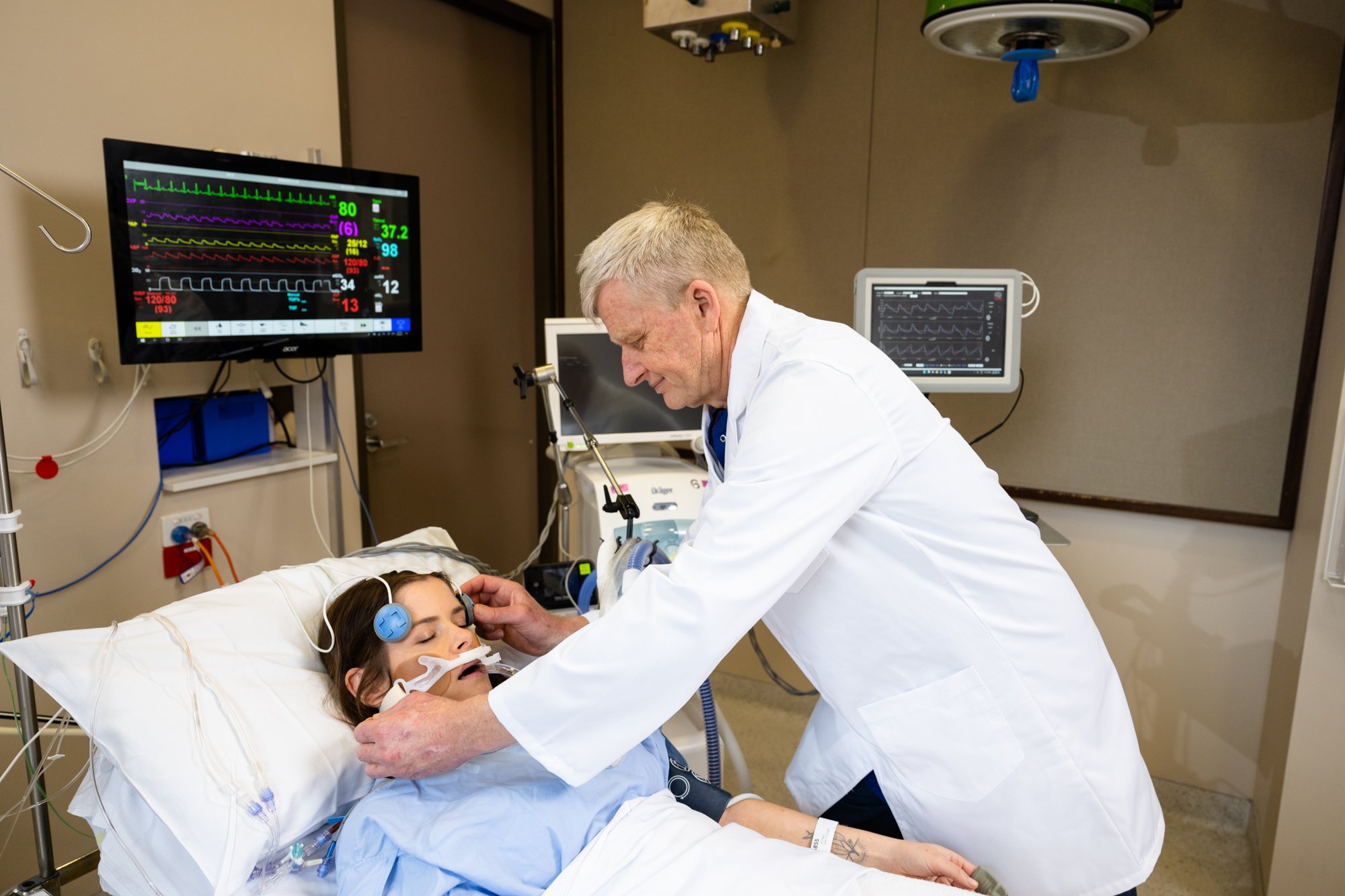
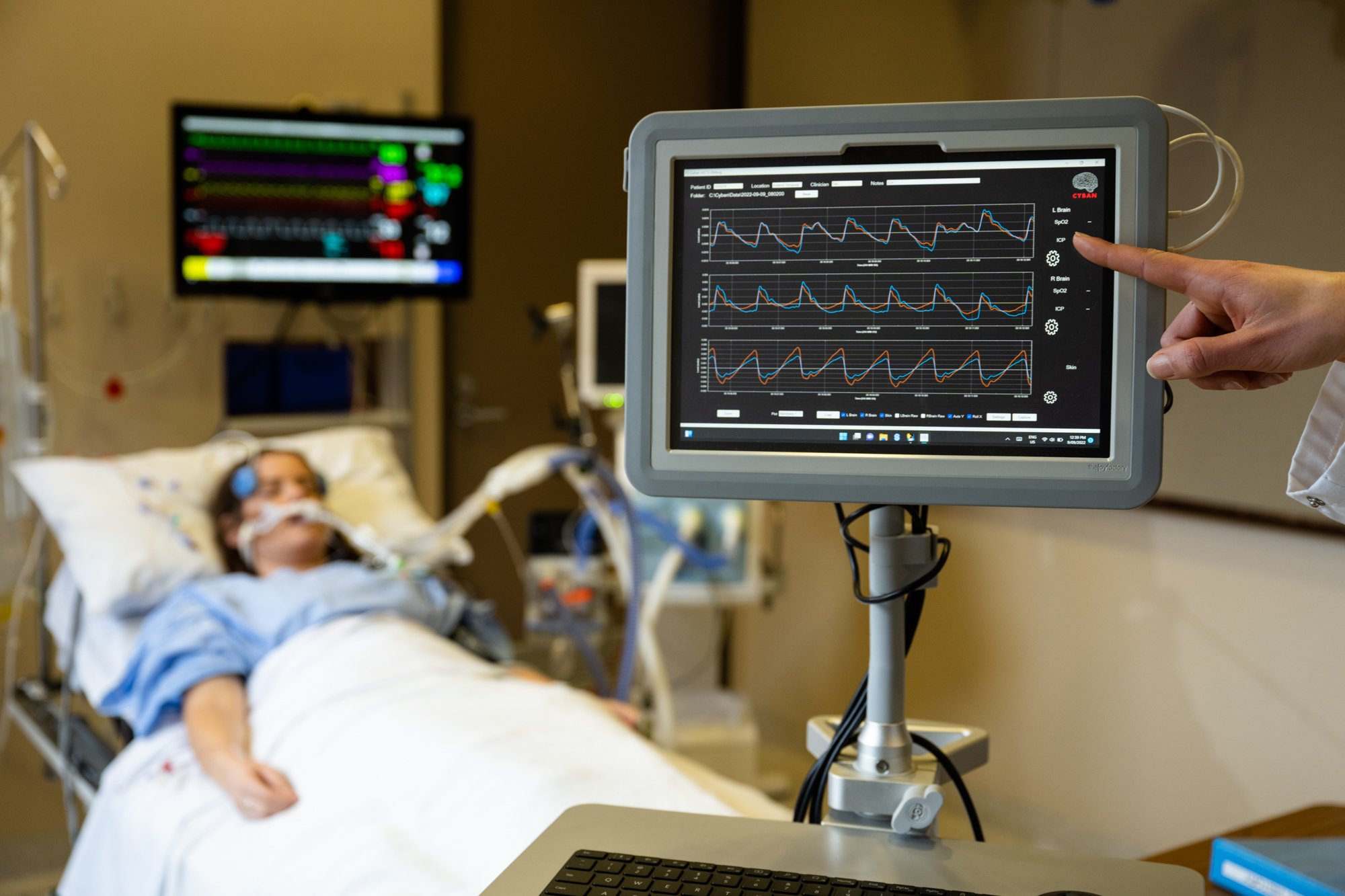
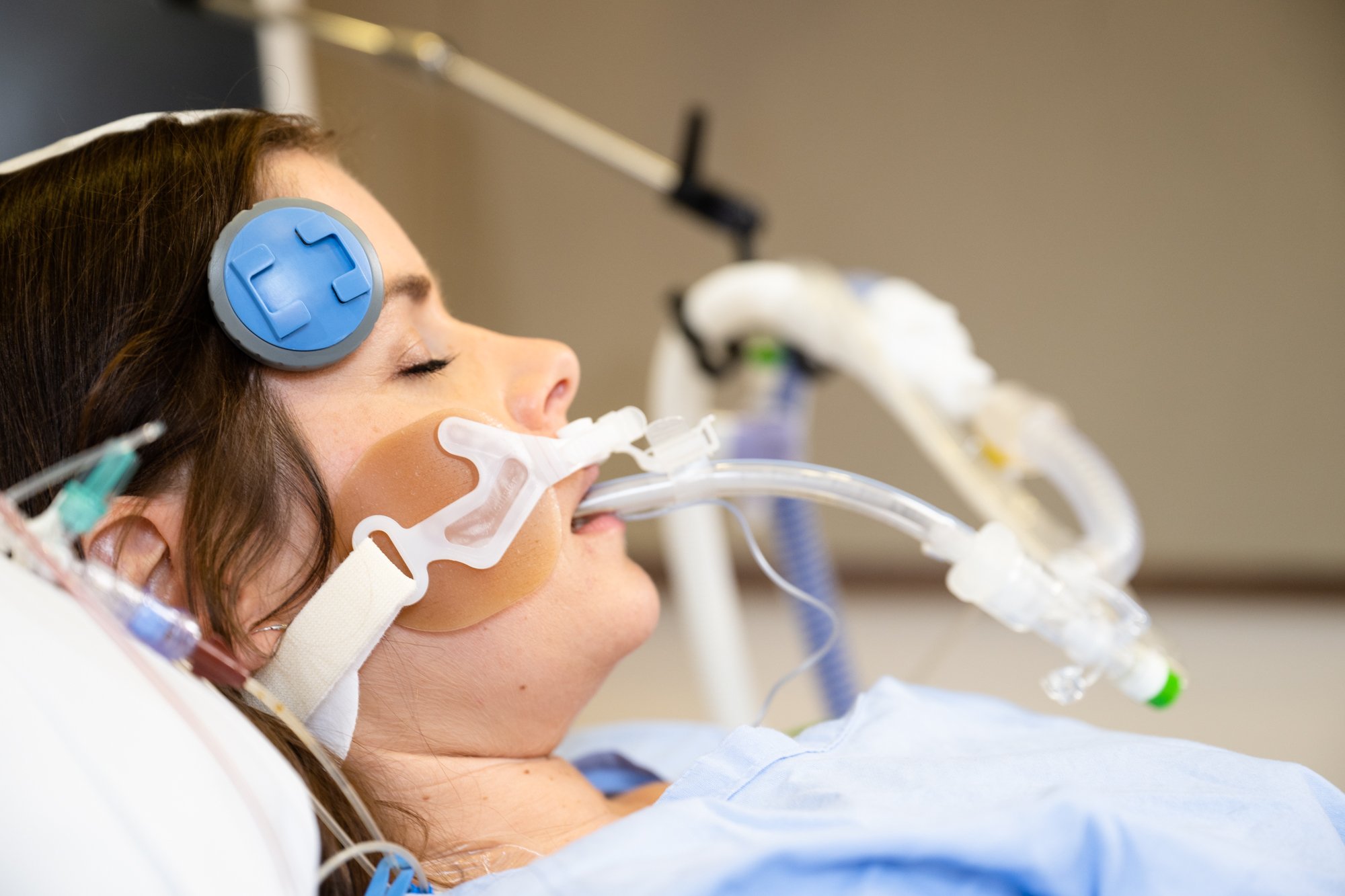
Cyban has developed a next generation brain oxygen monitor that advances the treatment of brain injuries by delivering reliable information continuously from the site of trauma to hospital discharge.
Our device reduces the need for invasive surgical procedures to provide accurate measurement of brain oxygen levels, delivering unprecedented brain oxygen monitoring in a user-friendly and non-invasive manner.
Delivering instant and continuous insights into the early detection of brain hypoxia enables Cyban to help reduce mortality and disability.
The device delivers accurate results quickly, to enable confident clinical care at every stage of the patient journey. This delivers valuable intelligence to intensive care and operating room staff who can improve the quality and efficiency of care provided to patients.
Reducing the need for invasive and costly surgical procedures enables hospitals to save costs and free up valuable resources.
By increasing diagnosis accuracy and accelerating treatment time, hospitals can reduce patient stays and improve patient outcomes simultaneously.